
By preserving the structure of the soil, Conservation Tillage methods contribute to improving the life of the soil and water management, as well as increasing biodiversity and carbon storage.
The structure of the soil is preserved and contains more organic matter
Conservation tillage offers several benefits. It improves soil health by preserving soil structure and organic matter, reduces erosion and runoff, and enhances water retention and drainage.
Better water management and less risk of erosion
Conservation tillage improves water management by enhancing moisture retention and reducing evaporation, thanks to crop residues acting as natural mulch. This practice also minimizes soil erosion by protecting the soil surface from wind and water, reducing runoff and maintaining soil structure
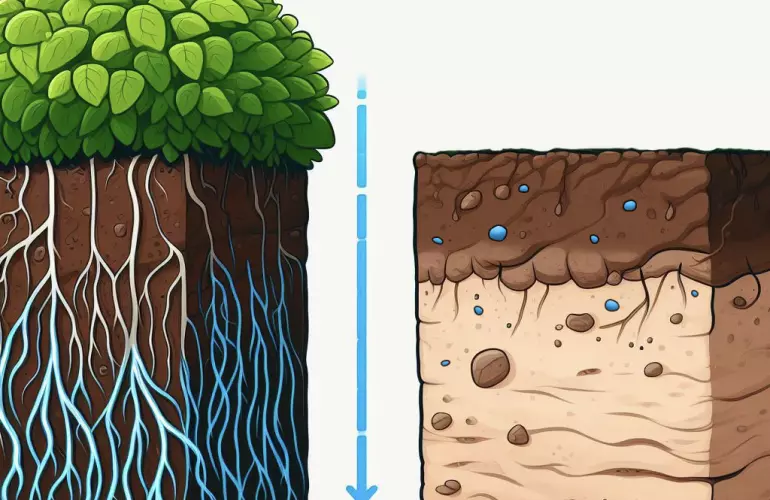
How do Conservation Tillage methods improve the structure of the soil?
Conservation tillage improves soil structure by preserving organic matter and reducing soil disturbance. This practice enhances soil aggregation, promotes microbial activity, and increases water infiltration. As a result, the soil becomes more resilient to erosion and compaction, supporting healthier plant growth.
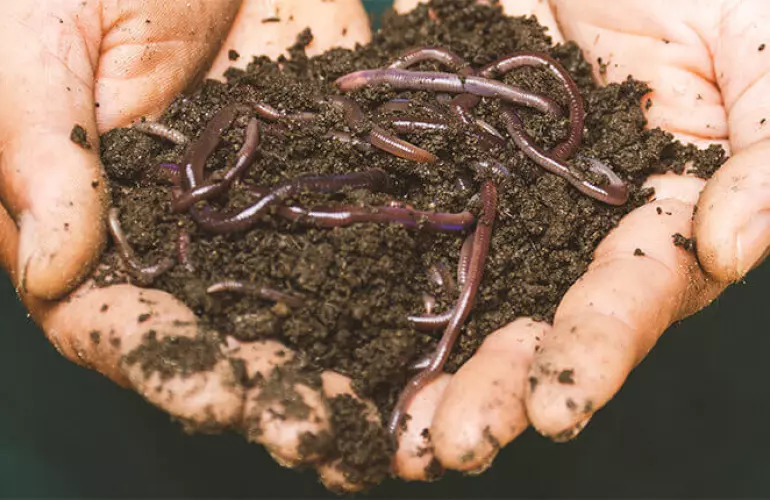
Renewed biological activity
The topsoil’s biodiversity is negatively affected when the soil is inverted. With conservation tillage, the content of organic matter in the surface layers of the soil increases which revives biological activity.

The downside of using chemicals to control weeds
No-till generally requires the use of chemicals to control weed growth. Mulch till and strip-till provide some weed control alleviating the need for intensive herbicide use.
